
What does nuclear power have to do with beauty pageants?
Well, brace yourself: It's electric.
The newly-crowned Miss America 2023, Grace Stanke, is championing this revolutionary cause.
The fusion of atomic science and pop culture, is kicking up renewed boldness among nuclear physicists coming out on social media, injecting a jolt of fresh energy into this age-old platform.
This coming-out-of-the-closet move is setting the stage for a pivot that could transform the global energy landscape.
New impetus for old tech
The use of nuclear to generate electricity is about 70 years old, powering the planet no matter the change of seasons. It had, of course, its share of highs and lows. But, till date, it's been mostly lows, thanks to bad PR.
At this pivotal moment, the nuclear power industry stands on the edge of a dramatic resurgence.
Given the looming specter of climate change, today's intrepid nuclear scientists find themselves crafting the future by drawing upon the wisdom of the past.
This provides a counterbalance to the loud "anti-nuclearism" of "green" parties (some of whom have now started favouring nuclear energy), the anti-proliferation lobby, and the doomsday peddlers citing Fukushima and Chernobyl at every turn.
Many countries and a growing number of privately-funded entities are re-evaluating the role of atomic chain reaction in the global energy mix.
These are some of the notable facts on the ground and recent industry developments:
1. Environmental benefits
- A small amount of uranium (1.1 kg) can provide a lifetime of energy to an average consumer, reducing the need for large amounts of coal and natural gas (88 tonnes of coal per average consumer).
- Nuclear power reduces global emissions by 1.5 gigatonnes and displaces 180 billion cubic meters of gas demand annually.
- More countries are embracing nuclear power as part their "energy mix".

2. Growing support
- France, the UK, Finland and Sweden are expanding their nuclear sectors. France aims to build 14 new reactors to become carbon neutral by 2050.
- In 2022, the Green Party in Finland voted in favor of nuclear power.
- In 2022, 7.9 GW of new nuclear power capacity was brought online, a 40 per cent jump on the previous year.
- China completed new two reactors in 2022.
- In 2021, nuclear plants supplied 2,653 TWh of electricity globally, up 4 per cent from 2,553 TWh in 2020.
- Public opposition to nuclear power has fallen below "boiling point" in the US, with at least 4 states lifting nuclear moratoriums.
- In Australia, the group Greens for Nuclear Energy declared: “We need nuclear energy to help stabilise our climate and reduce our ecological footprint.”
What propels this grand revival? It's nuclear's "firm-clean-power" credentials, an unmatched ability to generate carbon-free electricity when you want it, rather than relying on when the sun shines or the wind blows.
3. Safety and reliability
- Nuclear power has been used for over 70 years, providing a safe and reliable source of electricity.
- As of May 2023, there were 436 nuclear power reactors (NPR) in operation in 32 countries around the world.
- Despite incidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima, fatalities associated with nuclear power remain lower compared to fossil fuels and renewables.
- The average age of active nuclear reactors in the US is 42 years.

4. "Net Zero" Goals
- Nuclear power is seen as a key contributor to achieving "net zero" emissions by 2050 and decarbonising electricity and heat production.
- Improved safety measures and new reactor designs have made the 4th-generation reactors among the safest ever.
- Numerous design and technical iterations had been made in the industry as a whole that today’s “4th-generation” reactors are the safest than any previous ones.
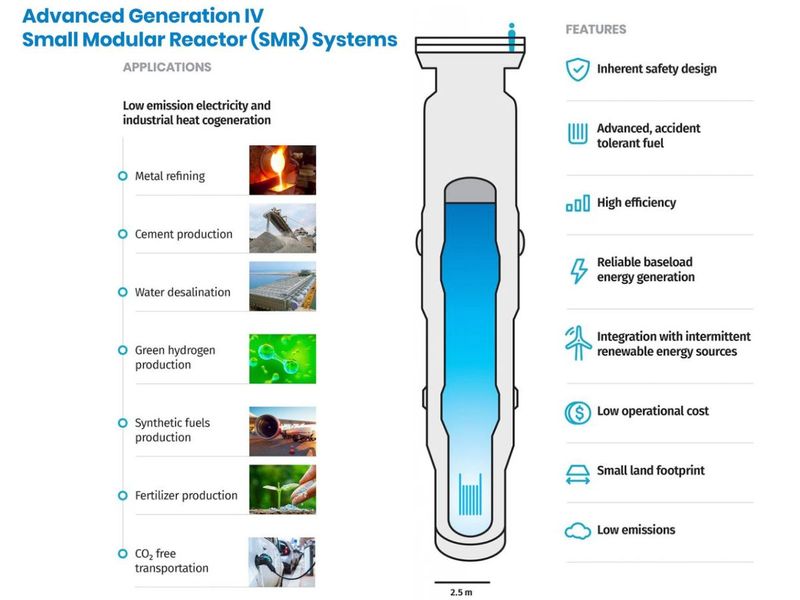
Improved safety measures and new reactor designs have made the fourth-generation reactors among the safest ever.
60
Number of reactors under construction globally (Source: Idaho National Lab)5. Advanced designs
- Solid-core reactors (fourth-generation) are at the forefront of nuclear technology development.
- Ongoing research aims to enhance their design and safety features.
- Solid-core reactors are designed to prevent accidents, reduce nuclear waste, resist proliferation, and offer economic efficiency.
- Reduced water requirements make them viable in regions with water scarcity.
435
Number of nuclear power reactors currently operating in 32 countries. (Source: Idaho National Lab)6. Market potential
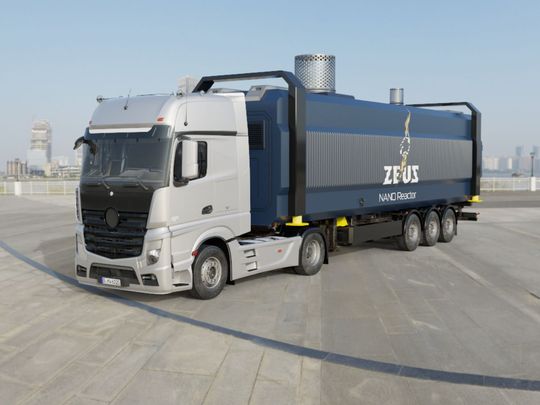
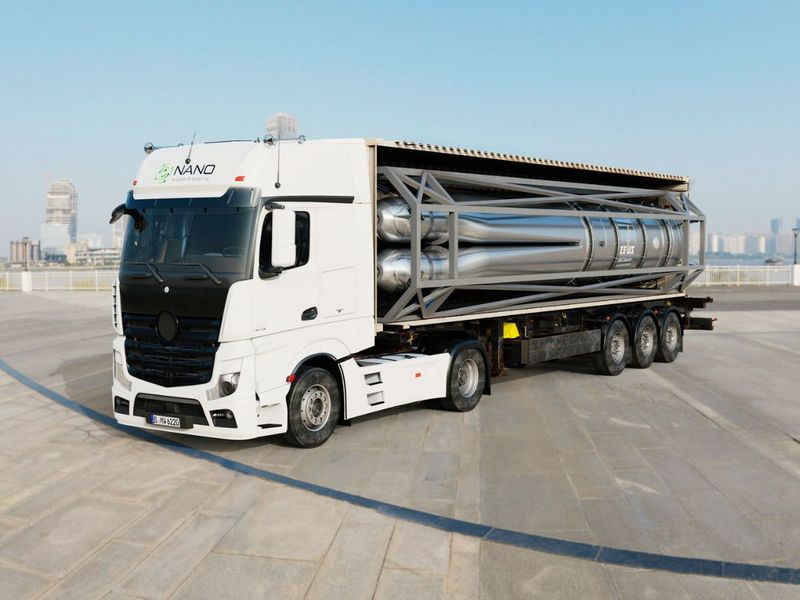
- The small modular reactor (SMR) market is expanding, offering more compact and versatile nuclear solutions.
- Jay Jiang Yu, founder of Nano Nuclear, predicts that micro-reactors (micro SMRs) could create an industry “1,000 times larger than Tesla”.
- SMRs offer a way to deliver nuclear power quickly, even in remote locations.

7. Global interest
- Big players like the US, Francce, Russia, China, Canada, the UK, India and South Korea are leading the nuclear resurgence.
- In Europe, nuclear is already the leading power generation solution
- Emerging nuclear markets in Central and Eastern Europe, Argentina, Australia Africa and Asia are actively pursuing SMR developments.
- Russia and Canada are leaders in SMR technology, leveraging its nuclear industry expertise.
150
Number of advanced nuclear projects globally in 2022 (Source: Third Way)8. Potential to replace diesel
- SMRs could replace diesel generators in applications like mine sites, military bases, disaster relief areas, and charging stations for electric vehicles.
- Jay Jiang Yu, founder of US company Nano Nuclear, which seeks to building “micro” SMRs, predicts the next-gen nuclear power would create an industry that will be “1,000x as big as Tesla.”
- He believes that micro reactors would be so economical they would rival diesel engines in cost and reliability.
Given the promise of nuclear energy, challenges remain — including regulatory and public acceptance, storage, and long-term non-proliferation concerns.
With advancements in SMRs and Generation IV nuclear reactors, coupled with better regulations, nuclear waste reuse and the pressing demand to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the latest iterations of harnessing nuclear power has the potential to play a significant role in delivering "firm clean power" across the globe in the near future.








