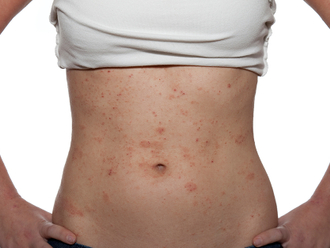
Overuse of antibiotics and routinely popping anti-inflammatory drugs could be dangerous for some people as these could trigger a life-threatening allergic reaction, warns a doctor.
The common triggers of allergies come from anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or aspirin or antibiotics such as penicillin, says Dr Ammar Al Douri, general practitioner, Medcare Hospital, Dubai. These drugs are available over the counter (OTC), and not always do they require a prescription.
“We get a number of patients with (drug) allergy symptoms,” he says, noting Medcare follows the policy of checking the patient’s history before prescribing any drugs.
“We first find out if a patient is allergic to any medication. Sometimes, there could be a strong reaction to a sulfa drug or Cox-2 inhibitor (a form of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug), and the patient’s airways become swollen (and he cannot breathe),” he says.
This situation is known as anaphylaxis or an anaphylactic reaction and could be life-threatening. The patient has to seek immediate medical intervention, he says.
Last year, a Filipina in Dubai suffered a horrible reaction after popping an antibiotic pill she bought from a pharmacy without a prescription, according to reports. It started with a rash and swelling over her body and then her skin started turning black and broke out in blisters. She had taken an antibiotic called Co-Amoxiclav Curan as she was suffering from flu and sore throat.
Doctors said she was suffering from Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis, a life-threatening skin disorder which leaves the skin looking as if it suffered severe burns. The Filipina later died after suffering for a week.
That, says Dr Al Douri, was an extreme case but he emphasises that self-prescription of antibiotics is highly dangerous. Always, he says, consult a doctor. The most common antibiotic, he says, is Penicillin which is used to control various infections such the upper respiratory tract and urinary tract infection and skin infection. “When you overuse an antibiotic, the bacteria becomes resistant to it and you cannot control the infection. The patient loses the benefit of that antibiotic and we have to shift to something else.”
If the use of antibiotics is not minimised in general, believes Dr Al Douri, there will be more incidents of allergies. “The misuse of antibiotics is common because people believe, wrongly, that without an antibiotic, their problem will never be resolved,” he says.
Asthmatics also need to be be aware that they could be sensitive to some drugs which could trigger an asthma attack, he says. “Aspirin-associated asthma can trigger wheezing.”
The other point to note about antibiotics and allergies is that even if a certain drug had not earlier triggered off a reaction, there is a still a possibility that it will do so in the future.
According to doctors, about 10 percent of adults with asthma are allergic to aspirin and other painkillers or to NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as ibuprofen, Motrin and Advil, which are generally used to reduce fever.
Asthma attacks caused by these drugs can be severe and must be avoided by those who are known to have aspirin-sensitive asthma.
Risk factors to drug allergy include frequent exposure to a drug or taking large doses, and a family history of developing allergies and asthma.
But why are some people more prone to allergies than others? Because, says Dr Al Douri, certain proteins such as immuneglobulines of type E (IgE) responsible for the fast adverse reaction are found in higher concentrations in these people’s blood.
However, there is no reliable blood or skin allergy test for drug sensitivity. Also, skin testing is best done by specialists as there is a risk of anaphylaxis. It may help diagnose an allergy to antibiotics such as Penicillin.