Google down: What happens when the site kicks up an error message?
Google search, website “froze” for thousands of users
Google, the world’s most popular search engine, has been a runaway success due to unique ability to provide higher-quality results for each user. It almost seems to intuitively understand your search intent, helping you find the most accurate and relevant information to match each query. It stands out from the competition.
But what would you do without Google?
A service outage on Tuesday (late Monday in the Americas) kicked off confusion and a deluge of memes — with netizens imagining what life would be like without Google.
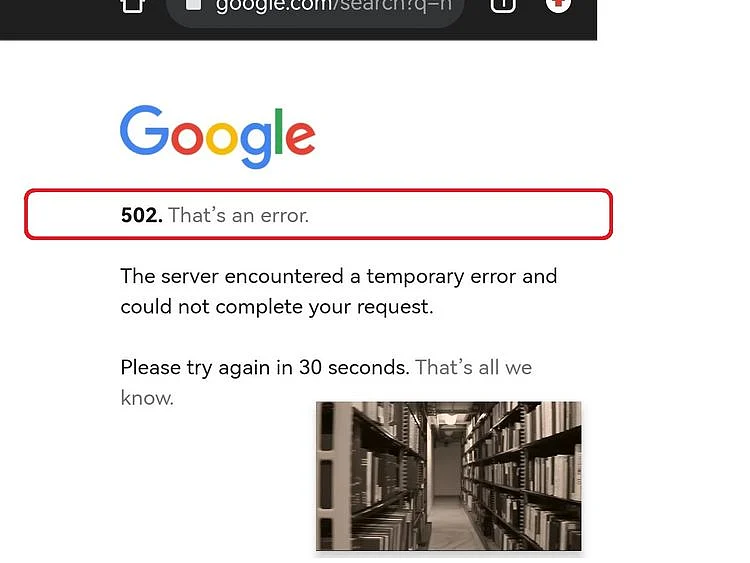
What happened?
Both Google’s website and search services temporarily stopped working for thousands of users on early Tuesday in the Asia (about 9pm Monday in New York).
The service appeared to be mostly restored before 10pm New York time.
Users in Asia reported the incident Tuesday morning (late night in the US) as the site and service went “down”. Downdetector, an outage-tracking service, reported service issues from around 9 pm (New York) on Monday.
An hour later, the tracker gathered more than 40,000 downtime reports.
The event is uncommon, but happens every now and then. Alphabet Inc.'s signature product, Google, is known for its high reliability, and disruptions are rare.
What Google services were affected and where?
Users reported problems with Google search, Gmail, Google maps and Google images.
Problems loading the Google website and performing searches were also observed in Taiwan and Japan, though the services appeared intermittently available.
What did Google say was the cause of the outage?
Google initially provided limited information.
Bloomberg reported an “electrical incident” at a Google facility in Iowa, US, on Monday. Social media reports have it that three people were sent to a nearby hospital, though it was not clear whether the event was related to the Google service outage.
A spokesperson told California news site SFGate: "We are aware of an electrical incident that took place today at Google's data center in Council Bluffs, Iowa, injuring three people onsite who are now being treated. The health and safety of all workers is our absolute top priority, and we are working closely with partners and local authorities to thoroughly investigate the situation and provide assistance as needed."
The company later said the problem stemmed from an “authentication system outage”, which lasted for around 45 minutes till 7.32am Eastern time.
“Today, at 3.47AM PT (Pacific time) Google experienced an authentication system outage for approximately 45 minutes due to an internal storage quota issue. This was resolved at 4:32AM PT,” Google said in a tweet.
“All services are now restored,” Google said in a statement. “We apologise to everyone affected, and we will conduct a thorough follow up review to ensure this problem cannot recur in the future.”
What are the most common causes of service outage?
The most common causes of such failures are the so-called "back-end web infrastructure". The incident is similar to those experienced by Fastly and Amazon Web Services last year.
Google downtime?
Following are the reported Google downtime incidents MAY 2009: Google reported downtime between 14:48 to 16:05 UTC on Thursday, May 14, 2009, during which some Google Apps users were unable to access their accounts. AUGUST 2013: Google and all of its services came down briefly for 2-3 minutes. The whole internet traffic went down by a massive 40%. OCTOBER 2018: A service outage affected YouTube in October 2018. AUGUST 2020: An incident occurred in August 2020 when Gmail/Google Drive outage was reported. DECEMBER 2020: On December 14, 2020, a global Google outage occurred. It affected users of most services: Gmail, YouTube, Google Drive, Google Docs, Google Calendar and Google Play. The glitch was caused by a failure in Google Accounts; services such as YouTube were still accessible with private browsing.
What happens to us when Google goes down?
Almost all of us work online. Some more than others. We use the Google search engine to browse the internet, but major companies, including Uber, Netflix and Twitter, rely heavily on Google services for work.
So when an outage occurs, just about everyone who uses the internet is affected. For a person, it makes internet browsing difficult, but they can shift to other search engines, including Microsoft’s Bings and DuckDuckGo, to surf the web.
Android users will be in a tizz. Other Google services that could be impacted are the popular Google Maps, News, Google Drive, Gmail and so on. Even platforms like YouTube would grind to a halt. Education too would be impacted as students, who log on to Google platforms for distance learning, will have an unexpected holiday.
Google runs the third-largest cloud-computing platform with data centres worldwide, and an outage could have disastrous consequences. Major companies that rely on Google services would take a massive hit. Any disruption to their services would wipe out millions in revenues.
What happens if Google goes down for one hour or one day?
A Google outage for an hour would sow panic in digital natives, who are perennially logged online. They will find their lives upended if the disruption lasts a day. The rage will explode on social media. Older people would cope better because they know there’s life outside the internet.
Users will find other ways of browsing the internet, which will mitigate the impact. They will live with the disruption for a day; it will be a day without maps, mails and movies. They will be forced to find alternatives. Soon they will realise that they can live without Google.
Not so for companies. It’s a nightmare situation for firms that rely on Google services. Even a five-minute disruption means loss in productivity and massive revenue loss. And a day’s outage will be so catastrophic that they will plan for a life beyond Google. That’s a situation Google can ill-afford.
Venture Beat reported that a five-minute outage in 2013 cost Google more than half a million dollars in revenue. Since the tech giant’s quarterly reported revenue in Q3 2020 was $46.02 billion, the recent interruption could have cost Google at least $47 million. That is $350,000 per minute. If Google had resolved the issue in five minutes, its revenue loss would have been less than $2 million, according to Coralogix, a software company.
Google will be just one of the hundreds of thousands of companies suffering from a loss of productivity. The five-minute Google disruption in 2013 resulted in a massive 40 per cent drop in internet traffic globally, according to Web analytics firm GoSquared. So imagine the situation if the outage lasts a day.
From BackRub to a trillion dollar company
Undoubtedly one the biggest inventions of our times, Google parries a whopping 90,000 search queries per second.
Celebrating its silver anniversary next year, the tech major has come a long way since it was co-founded by two Stanford grads — Larry Page and Sergey Brin – back in 1998. The project took shape on their university servers called BackRub.
In little over a year, it was popular enough to get its own hosting outside of Stanford. In 2004, Google went public – and there has been no looking back since. With a sharp focus and market domination over search engine technology, the firm has diversified into online advertising, cloud computing, quantum computing, e-commerce and consumer electronics.
Along the way, Google acquired huge companies like Motorola Mobility, YouTube, Waze, and HTC — tremendously increasing its influence, product line and profile. From email (Gmail) to navigation (Maps) and cloud computing (Cloud) to streaming (YouTube), Google is now ubiquitous in our quotidian digital lives.
Rated among the most visited websites, the American multinational has a valuation of $1 trillion.
Google’s chronology
1994: Larry Page and Sergey Brin meet at Stanford University. 1995: Page and Brin release Google on the Stanford server. 2000: Google releases 10 language versions: German, French, Danish, Swedish, Italian, Dutch, Portuguese, Norwegian, Spanish and Finnish. 2002: Google News is launched. 2004: The firm goes public with IPO. 2005: Google Earth, Google Maps and Google Talk launched. 2006: The company acquires video-sharing site YouTube. 2008: Launch of web browser – Google Chrome. 2010: Google markets its first Android phone – Nexus One. 2011: Larry Page takes over as CEO. Google Cloud launched. 2012: The tech major introduces Google Drive and Google Play. 2013: Google launches its chat platform – Hangouts. Chromecast is also launched. 2015: Google reorganises as a holding company – Alphabet. Larry Page becomes CEO of Alphabet, Sundar Pichai takes over as CEO of Google. 2017: Google buys HTC. 2018: Alphabet tops $100 billion in annual sales. 2019: Sundar Pichai becomes CEO of Alphabet. 2021: Google launches Tensor, its first chipset for smartphones.
Network Links
GN StoreDownload our app
© Al Nisr Publishing LLC 2026. All rights reserved.