Gulf nations urged to link seismic networks
Networks would provide a preliminary assessment of the seismic hazards in the region
Abu Dhabi: The Gulf nations including the UAE can tackle the possible threat of earthquakes more efficiently as the work towards linking the seismic networks of Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries is progressing.
"At present, there is no regular communication system to share the data including the earthquake location and strength. But an agreement to link the seismic networks of GCC countries will be discussed in the sixth Seismic Gulf Forum 2010 to be held in the capital from Monday to Thursday", a spokesman of the organisers told Gulf News on Wednesday.
"It is expected that all efforts will be made to conclude the agreement in the forum," said the spokesman of the National Centre of Meteorology and Seismology (NCMS) in Abu Dhabi, which organises the forum under the patronage of Shaikh Mansour Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Presidential Affairs and Chairman of the Board of Trustees of the NCMS.
Linking seismic networks will give a clearer picture of the seismic activity in the region, particularly along border areas, said a statement issued by the NCMS to Gulf News.
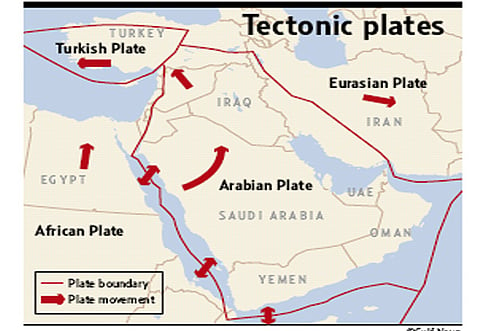
The seismicity of the Arabian plate will become clearer with the establishment of the seismic networks in the GCC countries. These networks would provide a preliminary assessment of the seismic hazards in the region.
The region is affected by the tectonics of the Arabian plate, where earthquakes occur along the plate collision boundaries, said the statement.
The northern and eastern boundaries formed and shaped by the folds of the Zagros Mountains of Iran and Turkey are known as one of the most seismically active areas in the world.
In addition, earthquakes are common occurrences in the Makran fault, close to the borders of the Arabian Gulf region, and where earthquakes as strong as magnitude 8 on the Richter scale could occur.
Co-operation in science, seismology, and seismic engineering at the global and regional levels is essential in order to reduce the risk of the impact of earthquakes.
The forum aims to promote cooperation and exchange of experience and knowledge among the countries of the Arabian Gulf and adjacent areas.
It also aims to raise awareness about engineering practices and the nature and causes of earthquakes, and their possible effects on the infrastructure, bringing the potential problems to the attention of planners and decision makers.
Major issues to be addressed
Linking the seismic networks of the GCC countries will address two major shortcomings:n At present there is no regular communication system to share data on earthquakesn A preliminary assessment of the seismic hazard in the region yet to be completed.
Potential threats
n The Zagros Mountains of Iran and Turkey are known as one of the most seismically active areas in the world.n Earthquakes are common occurrences in the Makran fault, close to the borders of the Arabian Gulf region, and where earthquakes as large as magnitude 8 (in Richter scale) could occur.
Forum
The sixth Gulf Seismic Forum 2010 will start at 8 am on Monday ( March 1) at Shangri-La Hotel in Abu Dhabi.
The first day is dedicated to the training course with lectures and exercises dealing with the calculation and mapping of seismic risk using Crisis 2007 software.
The sessions will begin with the opening ceremony on Tuesday (March 2 ), will continue on Wednesday and end on Thursday with the conclusion of the field trip.
— B.A.K
dummy header dum dummy dummy
The sixth Gulf Seismic Forum 2010 will start at 8 am on Monday ( March 1) at Shangri-La Hotel in Abu Dhabi . The first day is dedicated to the training course with lectures and exercises dealing with the calculation and mapping of seismic risk using Crisis 2007 software. The sessions will begin with the opening ceremony on Tuesday (March 2 ), will continue on Wednesday (March 3 ) 2010 and end on Thursday ( March 4th) with the conclusion of the field trip.
Tremors affecting the UAE
February 3, 2008: A series of tremors hit Ras Al Khaimah and Masafi area, which forced authorities to evacuate more than 800 students from two schools. The first earthquake measured 4.4 on the Richter Scale.
February 2, 2008: An earthquake measuring 3.4 on the Richter scale hit Dibba Al Fujairah at 5.44am. However, no injuries or damage to property was reported.
September 13, 2007: An earthquake hit Ras Al Khaimah and surrounding areas. It measured a magnitude of 4.6 on the Richter scale.
March 10, 2007: A moderate tremor and at least three aftershocks hit the UAE's East Coast, triggering panic and prompting residents in several areas of Fujairah and Ras Al Khaimah to run out of their homes.
June 29, 2006: A nighttime earthquake rocked southern Iran recorded as being between 5.4 and 5.6 on the Richter Scale jolted the Gulf region at about 1am and caused panic among many who felt the tremors. No damage was reported.
February 28, 2006: Residents in some high-rise buildings in Dubai and elsewhere in the UAE evacuated their premises after experiencing mild tremors at 11.31am.
— Compiled from Gulf News Archive
Aims
Timeline



