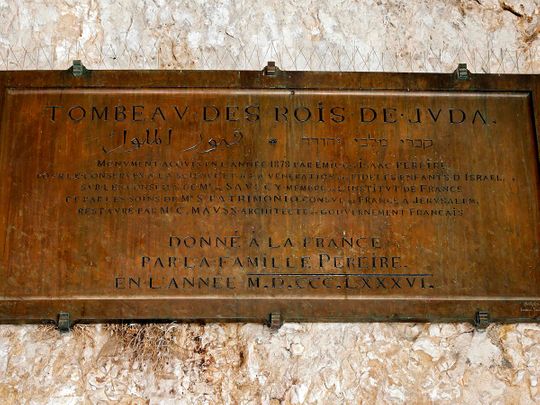
The Tomb of the Kings, a 2,000-year-old archaeological gem in the heart of Jerusalem owned by France, is to reopen to the public for the first time since 2010, the French consulate said Wednesday.
The elaborate Roman-era tomb with stone shelves that once held sarcophagi, considered among the largest in the region, will be opened on Thursday, and the following Tuesday and Thursday mornings, the consulate's website said.
Visits will be limited to 15 people in 45-minute stretches, the ticket order page said, noting the need for "proper dress" at the Tomb of the Kings, which is a funeral site.
The graves themselves will remain closed to the public for conservation and safety reasons.
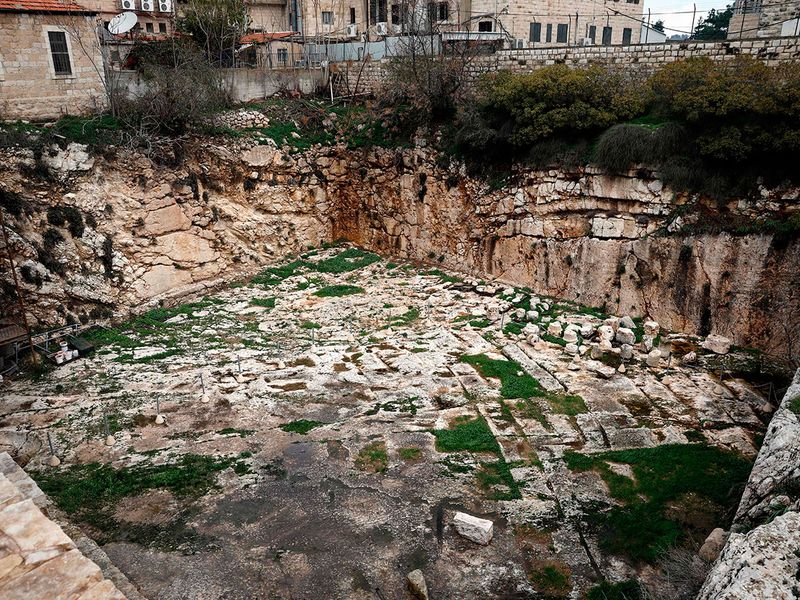
The vast site, located in east Jerusalem some 700 metres north of the Old City, is hidden behind a wall with a metal gate marked by a French flag.
It has been closed since 2010 due to renovations costing around a million euros ($1.1 million).
A spokeswoman for the French Consulate General said that in opening the site, France was implementing a decision and a commitment "made a long time ago".

Jews consider the tomb a holy burial site of ancient ancestors and demand the right to pray there.
Israel occupied mainly Palestinian east Jerusalem in the 1967 Six-Day War and later annexed it in a move never recognised by the international community.
It sees the entire city as its capital, while the Palestinians view the eastern sector as the capital of their future state.
Excavations of the site began in the 1860s, with Felicien de Saulcy of France taking on the project in 1863 and seeking to confirm it was the tomb of biblical figures King David and Solomon, giving rise to the site's name.
That theory has been ruled out, but the name has endured.
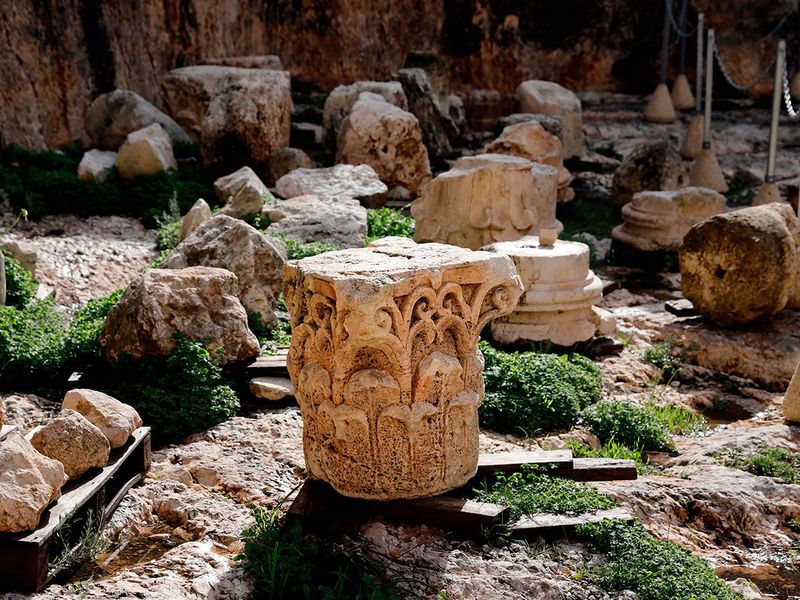

Several sarcophagi were found inside and are now in the Louvre museum in Paris, including one with an Aramaic inscription.
According to the most commonly accepted theory, it refers to Queen Helena of Adiabene, in today's Iraqi Kurdistan, and she may have built the tomb for her dynasty.
After de Saulcy's excavation, the tomb was purchased by the Pereire brothers, a Jewish banking family in Paris that would later hand the property over to France.
Israel and France had negotiated the site's status and reopening, but a French consulate spokeswoman declined to give details.
"We are reopening in accordance with the rules we set for ourselves," she told AFP.
Israel's foreign minister welcomed France's decision to open the tomb.












