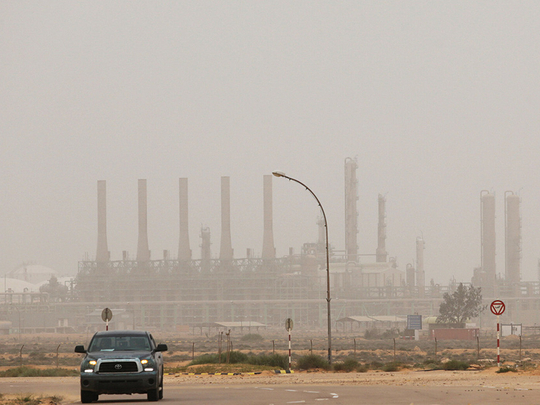
Tunis: Libya’s National Oil Corporation (NOC) has been coordinating with military forces from eastern Libya and has “no reason to believe” it will not regain control of the Es Sider and Ras Lanuf oil ports, NOC’s chairman said.
The loss and recapture of the ports this month by the eastern-based Libyan National Army (LNA) had raised doubts over its willingness to let the Tripoli-based NOC manage the ports.
Revenue from the sites is controlled by a central bank and UN-backed government in the capital which pro-LNA factions oppose.
Eastern officials accuse rivals in Tripoli and the western city of Misrata of supporting a March 3 attack on the ports by a faction known as the Benghazi Defence Brigades (BDB).
An oil guard commander appointed by the UN-backed government was deployed to secure them.
After they were retaken, the head of a Benghazi NOC office appointed by Libya’s eastern government said he was pulling out of an NOC unification deal signed in July and an LNA spokesman said there would be no immediate decision on a handover.
But in written responses provided to Reuters, Mustafa Sanalla, the Tripoli-based NOC chairman, said his staff had already been working with the LNA.
“We have been coordinating our assessment of the facilities with them,” Sanalla said, in his first public comments since the ports were retaken.
“We have no reason to believe control of the ports will not be handed back to NOC.” Es Sider and Ras Lanuf have a combined potential capacity of 600,000 barrels per day (bpd).
Revive output
Operations there and at two other ports southwest of Benghazi are crucial to the NOC’s efforts to revive Libya’s output, which has been crippled by years of conflict and political chaos.
The LNA took over the ports in September, ending a two-year blockade at three of them and quickly inviting the NOC to resume exports.
Es Sider and Ras Lanuf were badly damaged in previous rounds of fighting and have been operating well below normal levels.
The latest clashes, which included ground battles and more than a week of LNA air strikes, had dented the LNA’s claim it could defend the ports and led to fears that facilities would suffer further damage.
But Waha Oil Company resumed pumping to Es Sider on Saturday and Sanalla said the NOC had decided to restart operations at the ports based on technical assessments and a review by military engineers.
“For the most part, the facilities are not damaged. In one or two locations, some work needs to be done by the military engineers. Our workers are returning to their terminals gradually.” Reuters journalists observed little apparent additional damage to the ports during a visit on Thursday.
An engineer at the Waha oilfield said on Sunday it was pumping 25,000 bpd to Es Sider as it restarted production, which stood at 75,000 bpd before the clashes.
Sanalla said the NOC was hoping to raise overall production to 800,000 bpd by the end of April from 611,000 bpd currently.
Fragile gains
Libya along with Nigeria has been exempted from production cuts recently agreed by the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (Opec).
However, any gains in Libya remain fragile as long as the political turmoil that has fractured the country since its 2011 uprising continues.
Oil accounts for nearly all of Libya’s income and pipelines and ports have been repeatedly blockaded by local groups seeking political and financial gain.
Eastern authorities have attempted to sell oil independently, but have been blocked by international sanctions which remain in place.
Oil facilities are protected by the Petroleum Facilities Guard (PFG) but PFG units often operate independently or for a particular political faction.
Sanalla said a neutral PFG should have a role, “but under the authority and real management of NOC”.
“Putting the PFG under the NOC would, we think, go a long way to removing Libya’s oil assets as an object of military competition,” he said.
“Unless oil assets are taken off the table as an object of conflict, unless the oil industry is ring-fenced from our political conflict, then the possibility of more fighting remains.”