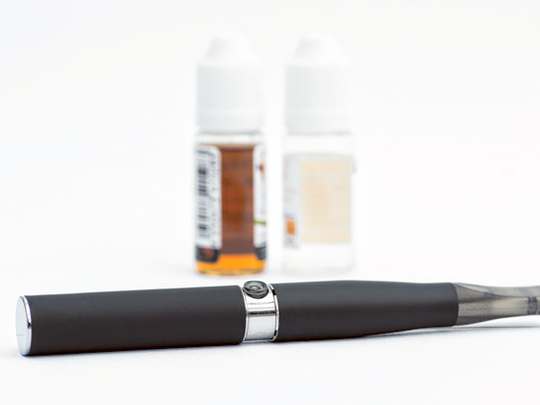
New York: A dangerous new form of a powerful stimulant is hitting markets around the world, for sale by the vial, the gallon and even the barrel.
The drug is nicotine, in its potent, liquid form — extracted from tobacco and tinctured with a cocktail of flavourings, colourings and assorted chemicals to feed the fast-growing electronic cigarette industry.
These “e-liquids,” the key ingredient in e-cigarettes, are powerful neurotoxins. Tiny amounts, whether ingested or absorbed through the skin, can cause vomiting and seizures and even be lethal. A teaspoon of even highly diluted e-liquid can kill a small child.
But, like e-cigarettes, e-liquids are not regulated by most authorities. They are mixed on factory floors and in the back rooms of “vamping” shops, and sold legally in stores and online in small bottles that are kept casually around the house for regular refilling of e-cigarettes.
Evidence of the potential dangers is emerging. Toxicologists warn that e-liquids pose a significant risk to public health, particularly to children, who may be drawn to their neon-bright colours and fragrant flavourings like cherry, chocolate and bubblegum.
“It’s not a matter of if a child will be seriously poisoned or killed,” said Lee Cantrell, director of the San Diego division of the California Poison Control System and a professor of pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco. “It’s a matter of when.”
Reports of accidental poisonings, notably among children, are soaring. Since 2011, there appears to have been one death in the United States, a suicide by an adult who injected nicotine. But less serious cases have led to a surge in calls to poison control centre. Across the US, the number of cases linked to e-liquids jumped to 1,351 in 2013, a 300 per cent increase from 2012, and the number is on pace to double this year, according to information from the National Poison Control Data System. Of the cases in 2013, 365 were referred to hospitals, triple the previous year’s number.
Last month, a two-year-old girl in Oklahoma City drank a small bottle of a parent’s nicotine liquid, started vomiting and was rushed to an emergency room.
That case and age group is considered typical. Of the 74 e-cigarette and nicotine poisoning cases called into Minnesota poison control in 2013, 29 involved children 2 and younger. In Oklahoma, all but two of the 25 cases in the first two months of 2014 involved children 4 and younger.
In terms of the immediate poison risk, e-liquids are far more dangerous than tobacco because the liquid is absorbed more quickly, even in diluted concentrations.
“This is one of the most potent naturally occurring toxins we have,” Cantrell said of nicotine. But e-liquids are available almost everywhere. “It is sold all over the place. It is ubiquitous in society.”
The surge in poisonings reflects not only the growth of e-cigarettes but also a shift in technology. Initially, many e-cigarettes were disposable devices that looked like conventional cigarettes. Increasingly, however, they are larger, reusable gadgets that can be refilled with liquid, generally a combination of nicotine, flavourings and solvents. In Kentucky, where about 40 per cent of cases involved adults, one woman was admitted to the hospital with cardiac problems after her e-cigarette broke in her bed, spilling the e-liquid, which was then absorbed through her skin.
The problems with adults, like those with children, owe to carelessness and lack of understanding of the risks. In the cases of exposure in children, “a lot of parents didn’t realise it was toxic until the kid started vomiting,” said Ashley Webb, director of the Kentucky Regional Poison Control Centre at Kosair Children’s Hospital.
Recreational use of liquid nicotine has in effect created an entire new drug category, and a controversial one. For advocates of e-cigarettes, liquid nicotine represents the fuel of a technology that might prompt people to quit smoking, and there is anecdotal evidence that is happening. But there are no long-term studies about whether e-cigarettes will be better than nicotine gum or patches at helping people quit. Nor are there studies about the long-term effects of inhaling vaporised nicotine.
Unlike nicotine gums and patches, there also is no regulation of e-cigarettes or their ingredients. The Food and Drug Administration has said it plans to regulate e-cigarettes but has not disclosed how it will approach the issue. Many e-cigarette companies hope there will be limited regulation.
“It’s the wild, wild west right now,” said Chip Paul, chief executive officer of Palm Beach Vapors, a Tulsa, Okla.-based company that operates 13 e-cigarette franchise nationwide and plans to open 50 more this year. “Everybody fears FDA regulation, but honestly, we kind of welcome some kind of rules and regulations around this liquid.”
Cynthia Cabrera, executive director of Smoke Free Alternatives Trade Association, said she would also favour regulations, including those that would include childproof bottles and warning labels, and also manufacturing standards. But she said many companies were doing that voluntarily, and that parents also needed to take some responsibility.
“You wouldn’t leave a bottle of Ajax out,” she said.
Advocates of e-cigarettes sometimes draw comparisons between nicotine and caffeine, characterising both as recreational stimulants that carry few risks. But that argument is not established by science, and many health advocates take issue with the comparison.
“There’s no risk to a barista no matter how much caffeine they spill on themselves,” said Dr. Neal L. Benowitz, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco, who specialises in nicotine research. “Nicotine is different.”
Without proper precautions, like wearing gloves while mixing e-liquids, these products “represents a serious workplace hazard,” he said. The nicotine levels in e-liquids varies. Most range between 1.8 per cent and 2.4 per cent, concentrations that can cause sickness, but rarely death, in children. But higher concentrations, like 10 per cent or even 7.2 per cent, are widely available on the Internet. A lethal dose at such levels would take “less than a tablespoon,” according to Cantrell, from the poison control system in California.
“Not just a kid,” he said. One tablespoon could kill an adult.”