Beirut (AP) Five years ago, Lebanese thronged the streets of Beirut to protest Syrian control over their country in a movement that quickly ended decades of military domination.
Now, many Lebanese are wondering if much has really changed. Syria's soldiers and the posters of its leader are gone but its influence is undeniably back.
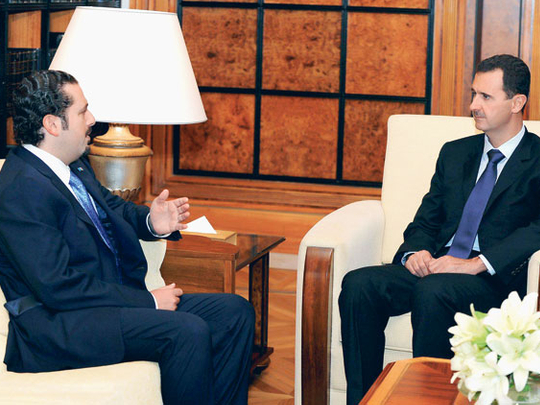
Western-backed Lebanese Prime Minister Sa'ad Hariri has shuttled to Damascus five times in the last nine months to try to repair relations that frayed after the 2005 Syrian withdrawal. For many in Lebanon, the trips harken back to times of Syrian dominance when Lebanese leaders used to travel frequently to Damascus to get marching orders.
Syria controlled Lebanon for nearly 30 years — something the US opposed — and kept about 35,000 troops on its soil. But everything changed in February 2005 when a massive truck bombing killed former Prime Minister Rafik Hariri, a billionaire businessman and father of the current prime minister.
Lebanon's anti-Syrian political bloc, which Sa'ad Hariri eventually came to lead, quickly accused Syria in the bombing. Millions of protesters turned out to demand Syria get out of Lebanon, in what was dubbed the "Cedar Revolution". Within months, Damascus pulled its troops out and Lebanese elections that followed swept anti-Syrian parties to power.
Weak leadership
Although officials have not said it openly, analysts say the current rapprochement appears to be an acknowledgment that Hariri is too weak to govern Lebanon without the support of his larger, more powerful neighbour.
Steadily rising Syrian influence in Lebanon culminated last week with a stunning reversal by Hariri. He said it was a mistake to blame Damascus for his father's assassination, adding the accusation had been politically motivated.
"Syria had been placed in the docket for the murder of [Hariri's] father ... and for him to look the world in the eye and say ‘I was wrong' — it's an extraordinary about-face," said Joshua Landis, an American professor and Syria expert who runs a blog called Syria Comment.
"We understand that the Cedar Revolution was a mirage," he added. "And so we have returned to the much more cynical but perhaps more realistic world of cutting deals and keeping all the local powers happy."
Hezbollah
Since the pullout, Syria has maintained its hand in Lebanon through its ally, Hezbollah, which has also been steadily gaining power. Hezbollah, also backed by Iran, is the strongest military force in the country and the main representative of its Shiite community, roughly a third of the population of 4 million.
The group has gained so much influence in the past few years it now has virtual veto power over government decisions.
Sectarian street clashes in 2008 pitting supporters of Hezbollah against Sunni rivals in Beirut may have helped convince Hariri that he needed Syria's help.
"He tried everything in his power to find a way of isolating Hezbollah and he couldn't do it," Landis said.
Hariri's allies have not said much publicly on his new stance regarding a possible Syrian role in his father's killing — an unusual silence suggesting they are unwilling to publicly criticise the prime minister's position.
A number of his allies in the US-backed coalition known as March 14, named for a day of massive anti-Syrian demonstrations in 2005, declined to comment when contacted over the past two days.
For Syria, it is also a remarkable transformation from the days when Damascus was isolated, ostracised and widely blamed for former Lebanese prime minister Rafik Hariri's assassination and other politically motivated killings in Lebanon.
The United States tried under the Bush years to keep Syria out of Lebanon's politics and largely failed. Now the administration of President Barack Obama has sought to improve ties with Damascus, and Syria's allies and opponents here say that has given it a freer hand to influence Lebanon.
And there have been signs that the Netherlands-based UN tribunal set up to try those responsible for Hariri's killing may have shifted attention away from Syria.
The tribunal has not yet named any individuals or countries as suspects. But in July, Hezbollah's leader said he expected the tribunal to indict members of his movement. He dismissed the allegations and said the tribunal has no credibility.
Tribunal
The first UN investigator into the Hariri assassination, Germany's Detlev Mehlis, said the plot's complexity suggested a role by the Syrian intelligence services and its pro-Syria Lebanese counterpart. But the two chief investigators who followed Mehlis have worked quietly and have not named any individuals or countries as suspects.