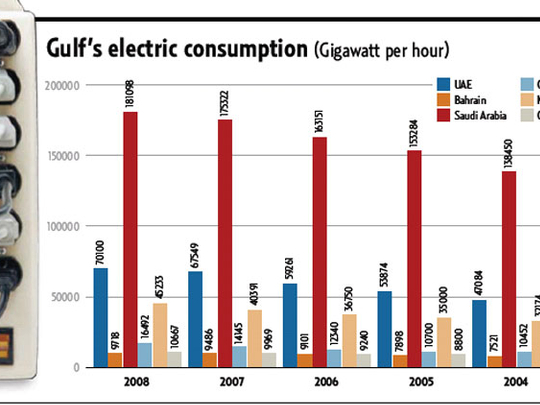
Dubai : Gulf countries are becoming increasingly involved in global efforts to promote sustainable, environment-friendly energy solutions as the region has been increasing at seven per cent annually, one of the highest growth rates in the world.
"As industries move forward through a period of significant changes, a parallel movement to adopt new green technologies and best practices that help cut down energy consumption and prevent energy wastage have subsequently been mobilised in the Gulf.
"Governments, in particular, are aggressively spearheading various energy-conservation campaigns such as a recent move by Dubai Government to implement stringent green building regulations for construction projects being built within the emirate.
"Even the UAE Government Strategy, which heralds a new phase of governance in the UAE, has specific provisions to increase the efficiency of energy consumption," Marco Gerazounis, Senior Vice-President of Software AG, said.
Project demand
He said additional investments worth around $25 billion (Dh91.8 billion) will be needed to address the projected demand by 2010.
Saudi Arabia will invest around $15 billion to generate 20,000 MW of additional power capacity, $5.1 billion by the UAE for an additional 3,400 MW, $2.5 billion by Kuwait to produce an additional 3,400 MW, $900 million by Bahrain to produce 1,200 MW, $800 million by Oman for 1,100 MW, and $600 million by Qatar for 800 MW more power.
He said one of the next-generation solutions that promote energy conservation is the smart metre.
This revolutionary intelligent metering solution, developed by Software AG in partnership with Siemens and other technology companies, will be a key component in the long-term campaign to reduce energy consumption, and will serve as a change agent that will forever redefine the way utility services are delivered to power consumers.
Information technology
The smart meter makes use of all kinds of information technology, including sensors and data transmission infrastructure, to communicate with the utility provider and process vital information in real time.
This creates exciting possibilities that were not available with the old metering system, such as allowing customers to detect a service outage, expose unauthorised use of electricity, or even change the maximum amount of electricity that a customer can demand at any time.
The smart meter even makes it possible for homeowners to check if they forgot to turn off any appliance while they are away, making it not just an invaluable energy-conservation tool, but also an important safety device for ordinary power consumers.
"Smart meters now have a prominent role in the energy conservation strategy of several developed countries, which are aiming to make smart metering technology the utility standard within the next 10 years. Italy, for instance, has seen the world's largest deployment with over 27 million utility customers using smart meters," Gerazounis said.
"The UK Government, on the other hand, has already revealed plans to fit every home with smart meters by the end of 2020. The smart meter technology has also been successfully implemented or is being gradually deployed in several other countries, including Japan, Canada, US, Australia, New Zealand, The Netherlands, Sweden, Finland, Denmark and Norway,"
Moreover, the smart meter system also allows both the utility provider and energy consumer to identify different patterns in energy use, which are vital information that will enable them to immediately respond to and correct wasteful energy practices or fix areas that are vulnerable to technical problems such as outages.
Potential
He said certain challenges, however, need to be hurdled for the smart meter technology to be successfully rolled out in the Gulf. Gerazounis explains: "Although we have seen smart meters being introduced in the region, particularly in the UAE, the full potential of this technology will remain untapped until the Gulf countries install the necessary infrastructure to implement the advanced functionalities of the smart metering technology.
"This is a great concern in the transition towards smart metering because quite often utility providers have disjointed IT systems, causing problems in scalability and the adoption of a new smart infrastructure.
"Considering the benefits of smart metering and the examples shown by other countries, it is unmistakable that smart metering is the inevitable future of the utility sector and a crucial element in efforts to conserve energy.
"And although the deployment of the smart metering system may take some time because of the required government legislation and adoption of customised technology infrastructure, it is clear that Gulf countries — being leaders and frontrunners in the field of energy — must immediately start the transition towards a more reliable, energy-efficient utility solution," he said.












