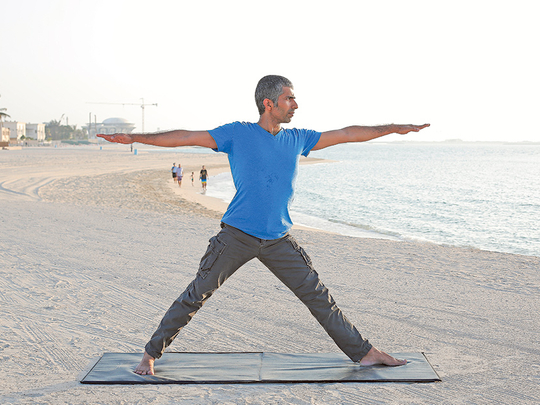
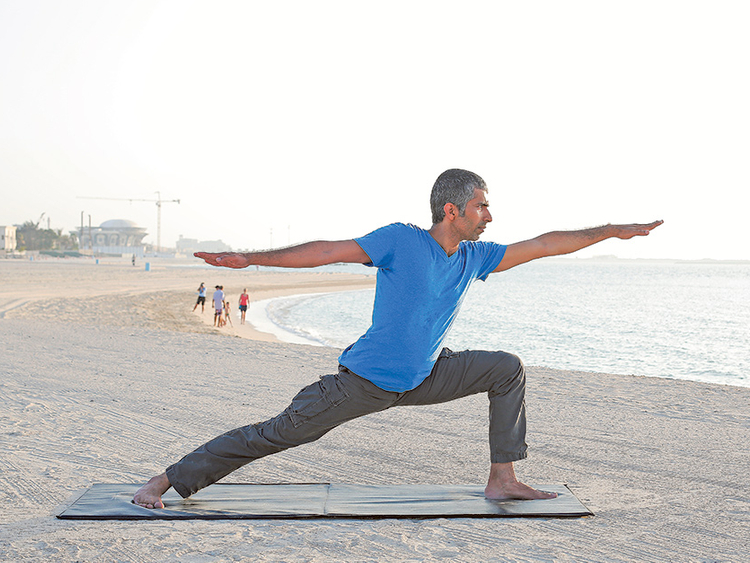
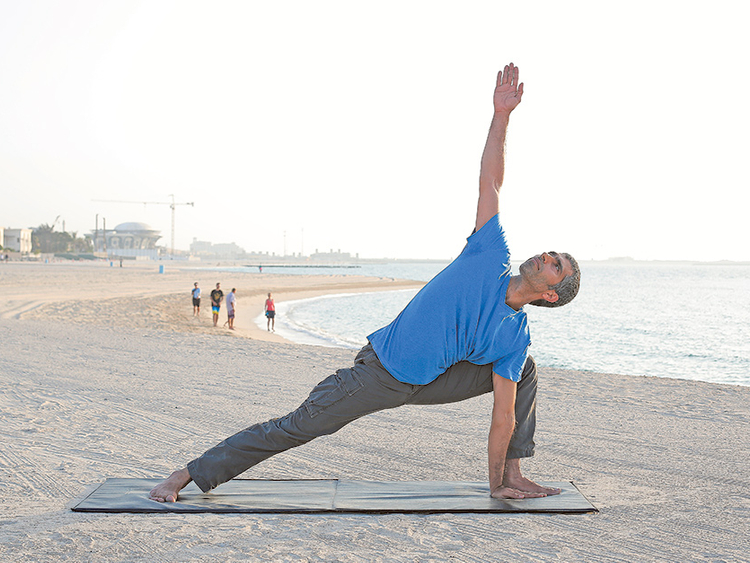
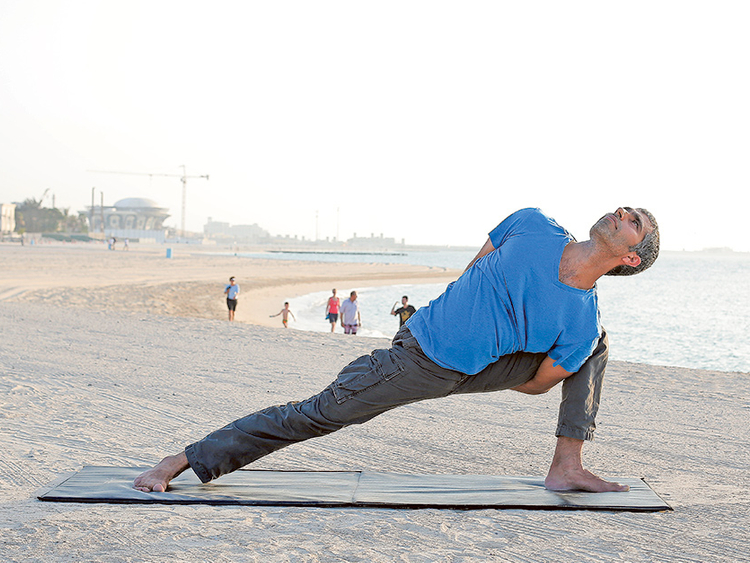
Scientists have figured out what ageing is, but how to reverse it or arrest it completely is not yet known. Several researchers have put together fragments of information and this is being used in generating creams, injections and supplements to address the ageing process, but this is clearly not enough. Further study is required into the side effects of these products in the long run.
Science has taken the approach of programmed theories and damage, or error theories, to understand ageing. Programmed theories such as programmed longevity, endocrine theory and immunological theory, emphasise that ageing follows a biological timetable and deterioration eventually leads to death. Damage or error theories such as wear and tear, rate of living, cross-linking, and free radicals, focus on environmental assaults that induce cumulative damage and eventually lead to cellular damage. These theories may interact with the other in a complex way and each theory comes with exceptions.
Factors that contribute to ageing
It is possible to understand broadly the various factors that affect ageing based on these theories.
Decline in cellular activity: In my previous column, Yoga: Introduction to Kayakalpa, we have understood ageing at the cellular level. It is observed that ageing can be a result of switching on and off of certain genes that lead to senescence (cell deterioration) and death. Research has also observed that as we grow older the cell membrane becomes less lipid (less watery and more solid). This impedes its efficiency to conduct normal function and in particular there is a toxic accumulation. Other research has studied the mitochondrial activity, which also affects cellular ageing. Thus rapid cellular repair and regeneration becomes essential.
Decline in endocrine function: Biological clocks act through hormones to control the pace of ageing. As the body ages, the endocrinal system does not function at its optimal level and sees a blatant decline at later stages of life.
Decline in immunity: Immune functions begin to decline over time, leaving the body largely susceptible to infections, diseases and death.
Free radical damage: The term free radical describes any molecule that has a free electron, and this property, which creates an extra negative charge, makes it react with healthy molecules in a destructive way. This imbalance makes the free radical bind itself to another balanced molecule as it tries to steal electrons. In doing so, the balanced molecule becomes unbalanced and thus a free radical itself. It is known that bad lifestyle is an accelerator of free radical production within the body. Free radicals cause damage to the macromolecular components of the cell, giving rise to accumulated damage causing cells, and eventually organs, to stop functioning.
Anti-ageing tips
Repair and nourishment of the body are essential on a daily basis.
Drink plenty of water every day. The cells need water to thrive.
Eat a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, nuts, grains and lean meat. Citrus fruits and berries can help detoxify the body. Vitamin C, found in these fruits, assists in collagen building and helps control the free radical damage.
Exercise at least 3-4 times a week.
Stay stress-free.
Next week: Kayakalpa: Secrets of age reversal, part 3.