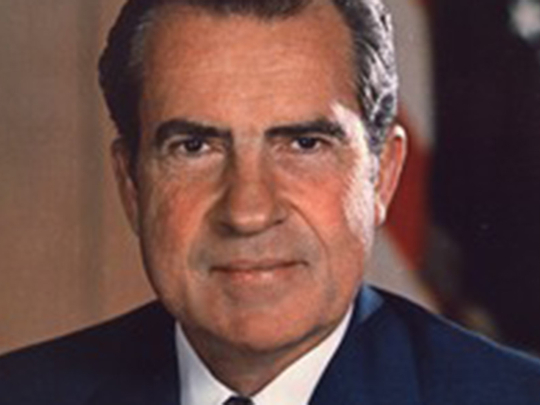
Richard M. Nixon always denied it: to David Frost, to historians and to Lyndon B. Johnson, who had the strongest suspicions and the most cause for outrage at his successor’s rumoured treachery. To them all, Nixon insisted that he had not sabotaged Johnson’s 1968 peace initiative to bring the war in Vietnam to an early conclusion. “My God. I would never do anything to encourage” South Vietnam “not to come to the table,” Nixon told Johnson, in a conversation captured on the White House taping system.
Now we know Nixon lied. A newfound cache of notes left by H.R. Haldeman, his closest aide, shows that Nixon directed his campaign’s efforts to scuttle the peace talks, which he feared could give his opponent, Vice President Hubert H. Humphrey, an edge in the 1968 election. On Oct. 22, 1968, he ordered Haldeman to “monkey wrench” the initiative.
The 37th president has been enjoying a bit of a revival recently, as his achievements in foreign policy and the landmark domestic legislation he signed into law draw favourable comparisons to the presidents (and president-elect) that followed. A new, $15 million facelift at the Nixon presidential library, while not burying the Watergate scandals, spotlights his considerable record of accomplishments.
Haldeman’s notes return us to the dark side. Amid the reappraisals, we must now weigh apparently criminal behaviour that, given the human lives at stake and the decade of carnage that followed in Southeast Asia, may be more reprehensible than anything Nixon did in Watergate.
Nixon had entered the fall campaign with a lead over Humphrey, but the gap was closing that October. Henry A. Kissinger, then an outside Republican adviser, had called, alerting Nixon that a deal was in the works: If Johnson would halt all bombing of North Vietnam, the Soviets pledged to have Hanoi engage in constructive talks to end a war that had already claimed 30,000 American lives.
But Nixon had a pipeline to Saigon, where the South Vietnamese president, Nguyen Van Thieu, feared that Johnson would sell him out. If Thieu would stall the talks, Nixon could portray Johnson’s actions as a cheap political trick. The conduit was Anna Chennault, a Republican doyenne and Nixon fund-raiser, and a member of the pro-nationalist China lobby, with connections across Asia.
“! Keep Anna Chennault working on” South Vietnam, Haldeman scrawled, recording Nixon’s orders. “Any other way to monkey wrench it? Anything RN can do.”
Nixon told Haldeman to have Rose Mary Woods, the candidate’s personal secretary, contact another nationalist Chinese figure — the businessman Louis Kung — and have him press Thieu as well. “Tell him hold firm,” Nixon said.
Nixon also sought help from Chiang Kai-shek, the president of Taiwan. And he ordered Haldeman
to have his vice-presidential candidate, Spiro T. Agnew, threaten the CIA director, Richard Helms. Helms’s hopes of keeping his job under Nixon depended on his pliancy, Agnew was to say. “Tell him we want the truth — or he hasn’t got the job,” Nixon said.
Throughout his life, Nixon feared disclosure of this skulduggery. “I did nothing to undercut them,” he told Frost in their 1977 interviews. “As far as Madame Chennault or any number of other people,” he added, “I did not authorise them and I had no knowledge of any contact with the South Vietnamese at that point, urging them not to.” Even after Watergate, he made it a point of character. “I couldn’t have done that in conscience.”
Nixon had cause to lie. His actions appear to violate federal law, which prohibits private citizens from trying to “defeat the measures of the United States.” His lawyers fought throughout Nixon’s life to keep the records of the 1968 campaign private. The broad outline of “the Chennault affair” would dribble out over the years. But the lack of evidence of Nixon’s direct involvement gave pause to historians and afforded his loyalists a defence.
Time has yielded Nixon’s secrets. Haldeman’s notes were opened quietly at the presidential library in 2007, where I came upon them in my research for a biography of the former president. They contain other gems, like Haldeman’s notations of a promise, made by Nixon to Southern Republicans, that he would retreat on civil rights and “lay off pro-Negro crap” if elected president. There are notes from Nixon’s 1962 California gubernatorial campaign, in which he and his aides discuss the need to wiretap political foes.
Of course, there’s no guarantee that, absent Nixon, talks would have proceeded, let alone ended the war. But Johnson and his advisers, at least, believed in their mission and its prospects for success.
When Johnson got word of Nixon’s meddling, he ordered the FBI to track Chennault’s movements. She “contacted Vietnam Ambassador Bui Diem,” one report from the surveillance noted, “and advised him that she had received a message from her boss … to give personally to the ambassador. She said the message was … ‘Hold on. We are gonna win. … Please tell your boss to hold on.’”
In a conversation with the Republican senator Everett Dirksen, the minority leader, Johnson lashed out at Nixon. “I’m reading their hand, Everett,” Johnson told his old friend. “This is treason.”
“I know,” Dirksen said mournfully.
Johnson’s closest aides urged him to unmask Nixon’s actions. But on a Nov. 4 conference call, they concluded that they could not go public because, among other factors, they lacked the “absolute proof,” as Defense Secretary Clark Clifford put it, of Nixon’s direct involvement.
Nixon was elected president the next day.
— John A. Farrell is the author of the forthcoming “Richard Nixon: The Life.”