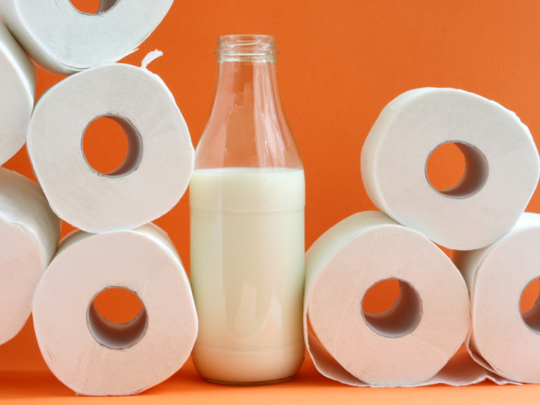
What is Lactose-free milk?
Lactose-free milk is cow milk with added natural enzyme lactase, an enzyme that breaks down the milk-sugar lactose into more easily digestible sugars, glucose and galactose, so it’s easier to digest. Milk does have lactose, which is the naturally occurring sugar. The lactose in milk is hard to digest for some people (lactose intolerant), so adding the lactase enzyme breaks down the lactose into sugars making it more digestible for them. Therefore, since the lactose is converted to sugar, the term “lactose free”.
Is lactose-free milk real milk?
Lactose-free milk is real milk. The enzyme lactase has been added to break down the lactose, the natural sugar found in milk. Lactose-free milk and other dairy products allow people with lactose intolerance to enjoy drinking milk and eating dairy foods. Lactose-free cow’s milk, offers strong health benefits.
Nutrients: Lactose-free milk contain the same amount of calcium, vitamin A, vitamin D and protein as regular milk and dairy products.
Health benefits: Drinking lactose-free milk can prevent the symptoms of lactose intolerance. Helps in the development of strong bones and teeth.
Helps build and repair muscle tissue Vitamin D –helps in the absorption of calcium. Important for good vision, healthy skin and immune system.
Plays an important role in nerve function, muscle contraction and blood clotting.
Tips to include in diet: Add fortified lactose-free milk to your whole grain cereal for breakfast. As a snack, drink a glass of lactose-free milk every day. Lactose-free milk can also be used in soups, milkshakes, smoothies, lactose-free sauces, salad dressings, stews and desserts.
Tips to choose: Choose: 100% lactose-free milk. Look for brands fortified with calcium vitamin D.
Cooking techniques: Lactose-free milk works well with all recipes in place of regular milk.
Calories
Lactose free milk (calcium fortified) 1 cup = 90 Kcal
What is lactose intolerance?
Lactose intolerance is the inability or insufficient ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and milk products. Lactose intolerance is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme lactase, which is produced by the cells lining the small intestine. Lactase breaks down lactose into two simpler forms of sugar called glucose and galactose, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream.
Lactose intolerance is a common digestive problem where the body is unable to digest lactose, a type of sugar mainly found in milk and dairy products.
Symptoms of lactose intolerance include:
• a bloated stomach.
• flatulence (wind).
• diarrhoea.
What is milk allergy?
Cow’s milk allergy and lactose intolerance are different. Milk allergy is a reaction by the body’s immune system to one or more milk proteins and can be life-threatening when just a small amount of milk or milk product is consumed. Milk allergy most commonly appears in the first year of life, while lactose intolerance occurs more often in adulthood.